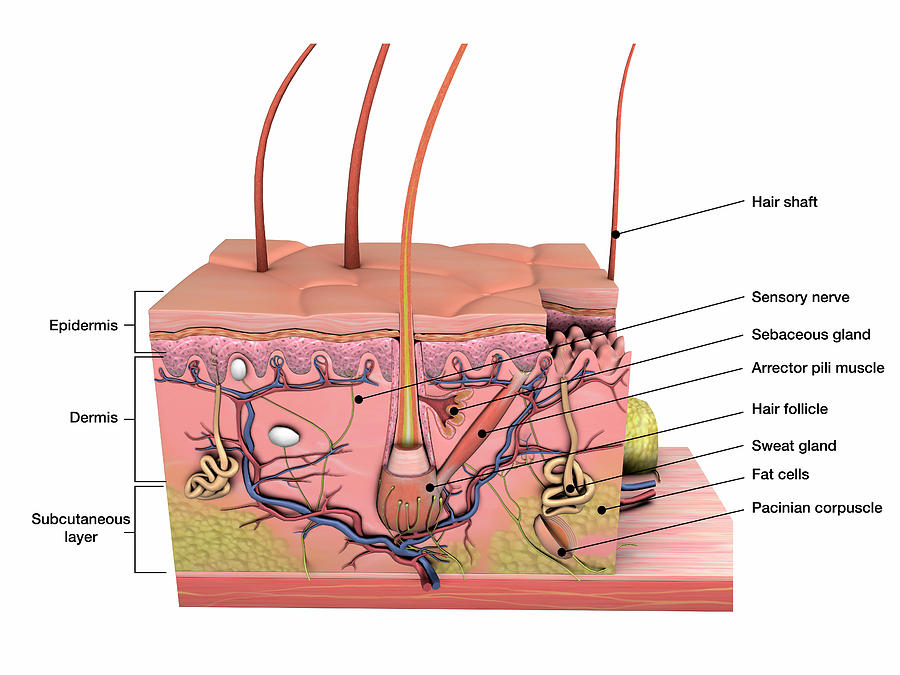
Anatomy Of Human Skin With Labels Photograph by Hank Grebe Pixels
'Skin Diagram || How to draw and label the parts of skin' is demonstrated in this video tutorial step by step.The sense of touch had received supreme importa.
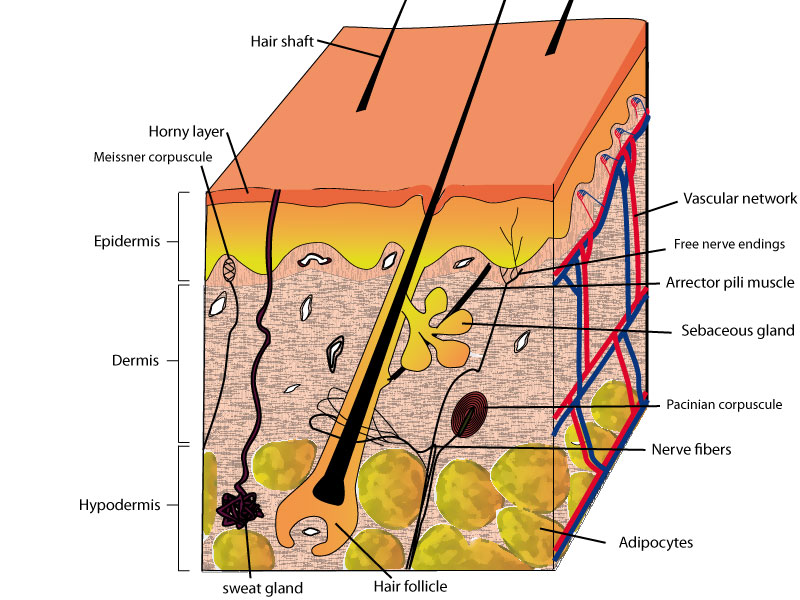
Normal human skin [Biologie de la peau]
Skin diagram unlabeled Skin anatomy Specialized integumentary system quizzes Sources + Show all Integumentary system quiz and answers One of the best ways to start learning about a new system, organ or region is with a labeled diagram showing you all of the main structures found within it.

The structure of the skin is composed of two layers (1) the epidermis... Download Scientific
Functions. The skin has a significant capacity for renewal and crucial roles for the normal functioning of the human body. It is an effective barrier against potential pathogens and protects against mechanical, chemical, osmotic, thermal and ultraviolet radiation damage (through melanin). The skin also takes part in a variety of biochemical synthetic processes, such as vitamin D production.

Skin Definition, Structure And Functions Of Skin
Dermis. Definition. Fibrous and elastic tissue, provides strength and elasticity to the skin and supports the epidermis, home to hair follicles, glands, nerves etc. Location. Term. Papillary Layer. Definition. Upper dermal layer, provides the epidermis with nutrients and regulates body temperature. Location.
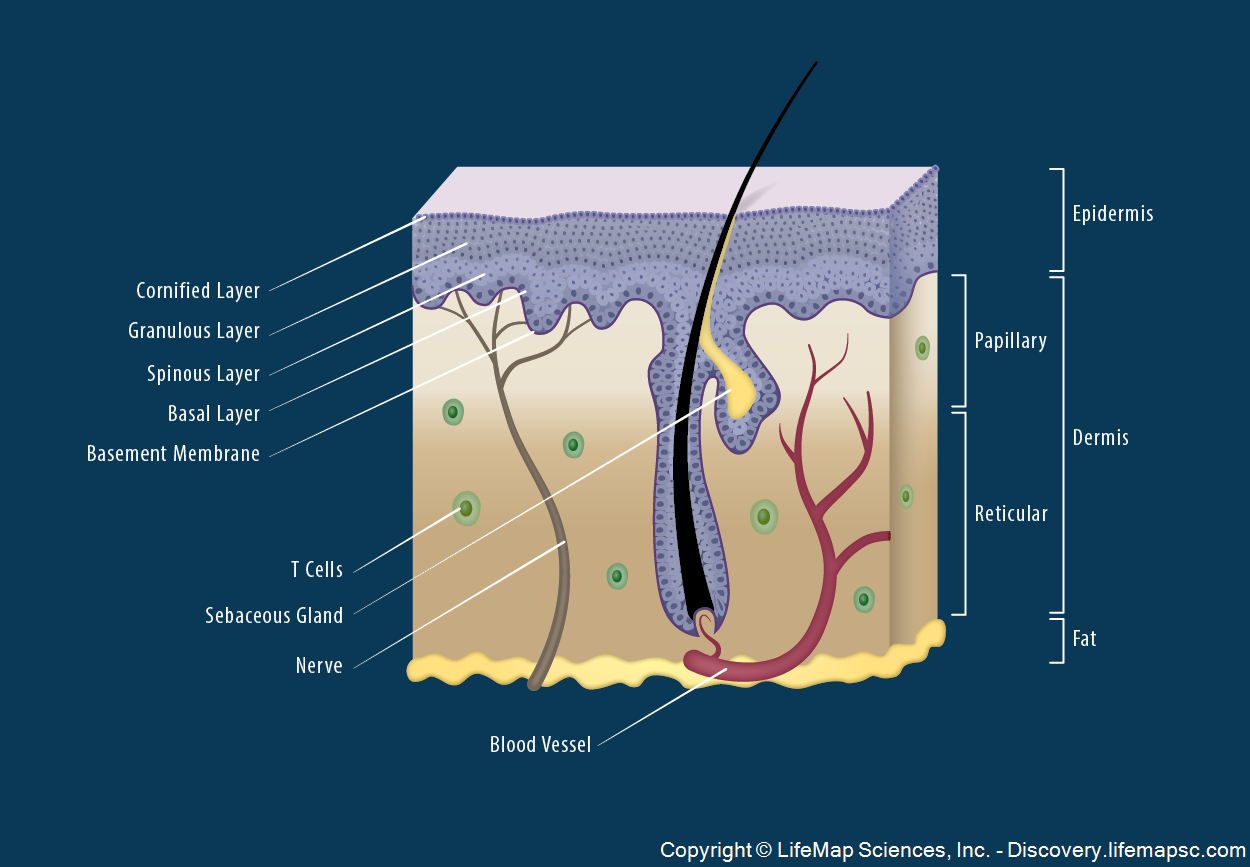
Skin Structure infographic LifeMap Discovery
This online quiz is called label the skin diagram. It was created by member k8e1404 and has 12 questions.
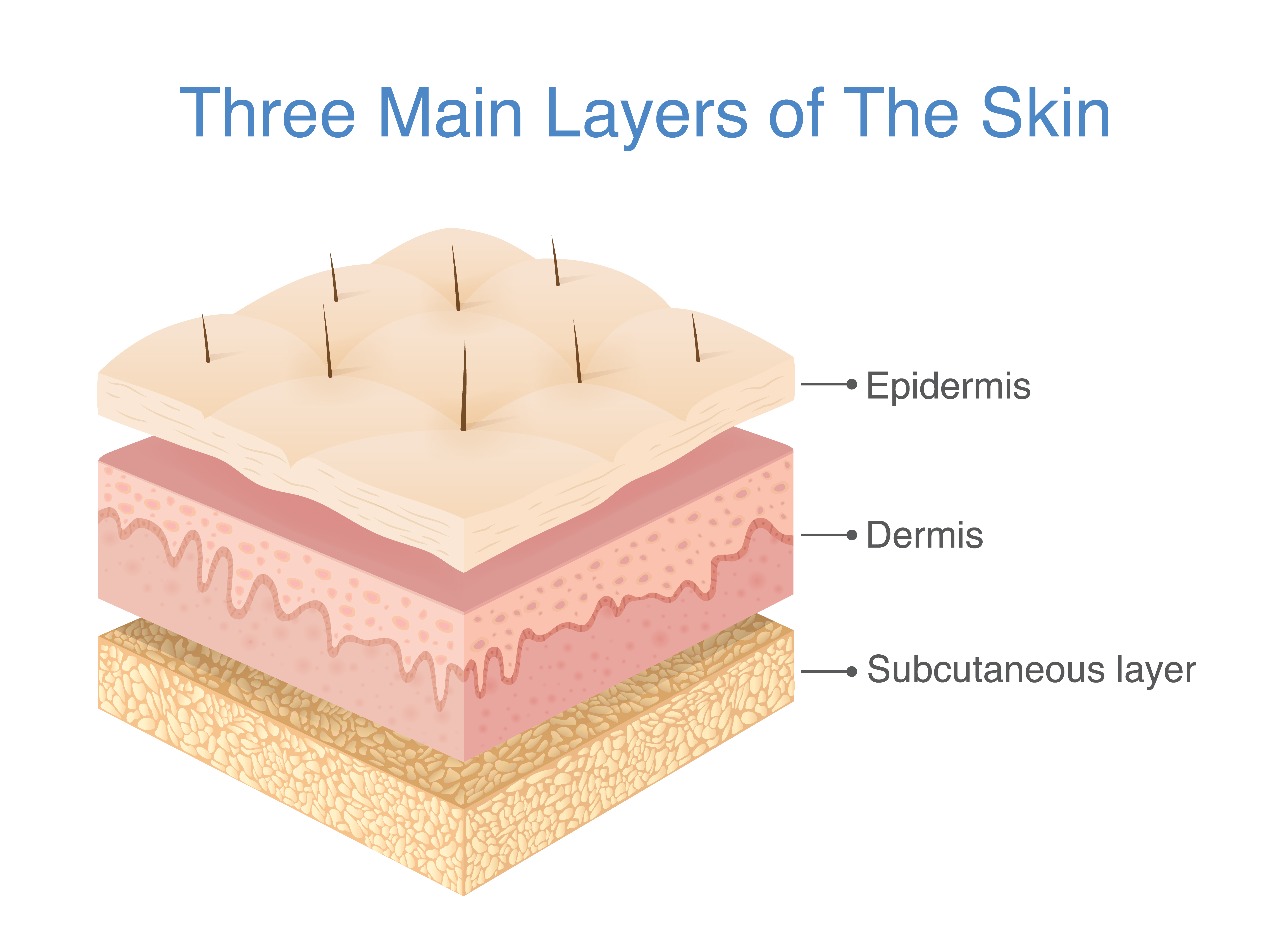
What Are The 3 Layers Of Skin? SkinMindBalance
Skin Diagram Labeling . 1. Label the diagram with the . letters. below according to the structure/area they describe. You may label with a line or put the label directly onto the area described. Be as precise as possible. If you are worried about the precision of your label add a word after to explain exactly where your label should be.
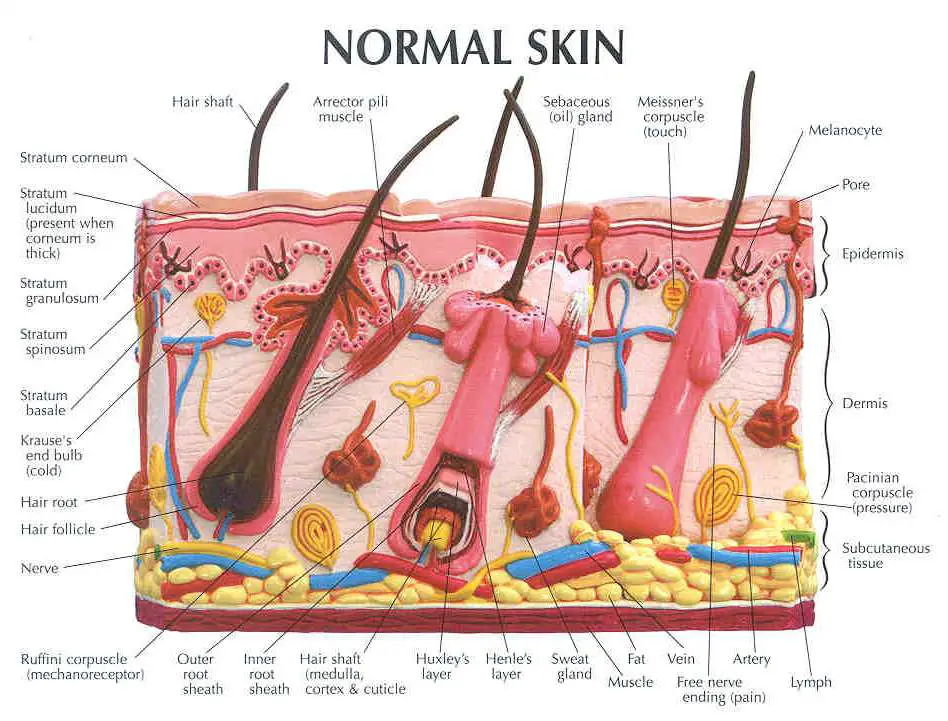
Skin diagram labeled
Definition Middle layer of the skin; contains collagen; location of sweat & sebaceous glands and nerve endings and capilaries Location Term Epidermis Definition outermost layer of the skin;composed of squamous epithelium; contains keratin Location Term subcutaneous layer Definition

loadBinary_006.gif (992×779) Skin anatomy, Integumentary system, Human integumentary system
Figure 1. The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose connective and fatty tissues.

34 Label The Skin Diagram Labels 2021
Biology Important Diagrams Skin Diagram Skin Diagram The largest organ in the human body is the skin, covering a total area of about 1.8 square meters. The skin is tasked with protecting our body from external elements as well as microbes. Interesting Note:
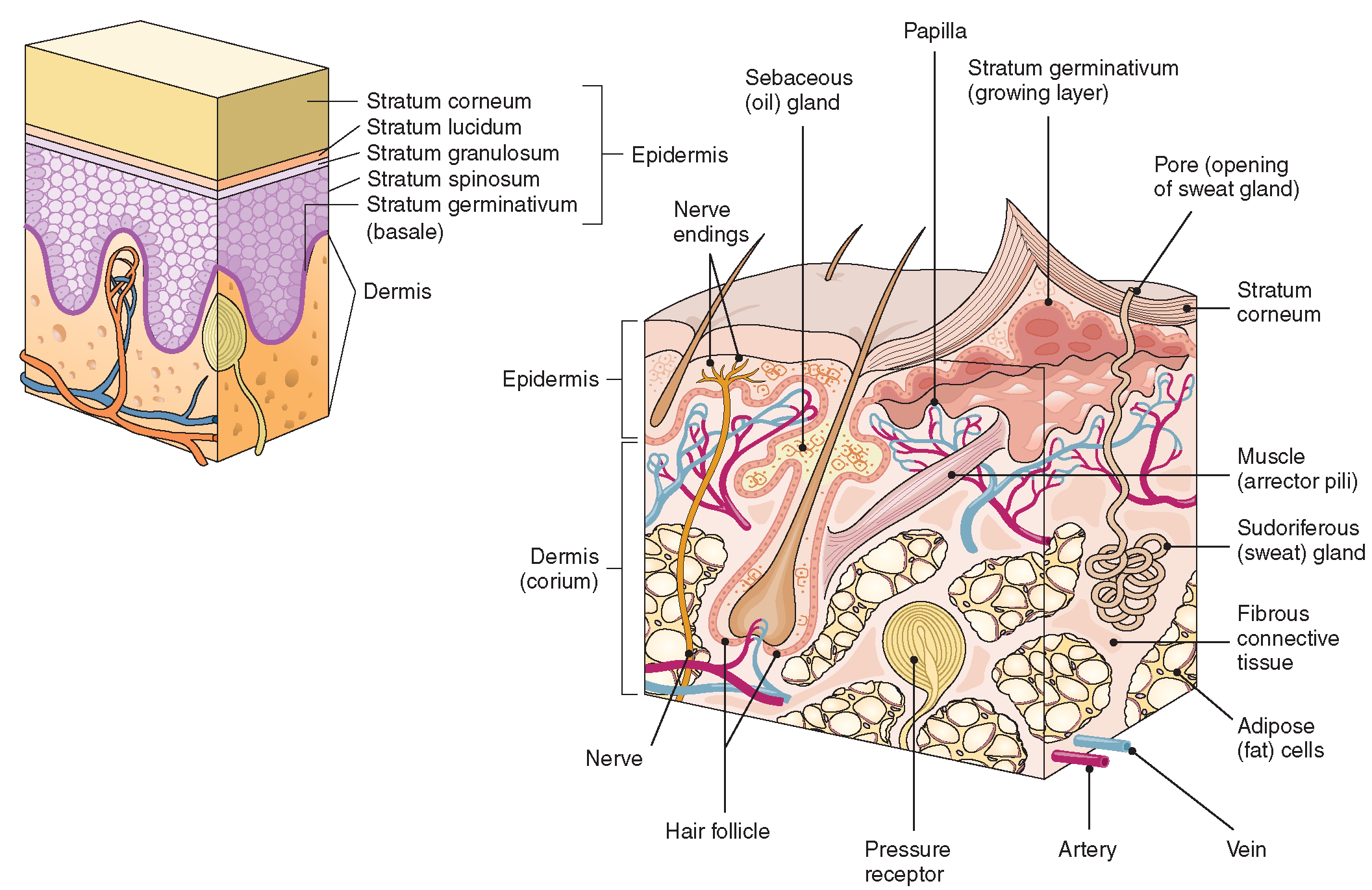
The Integumentary System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 1
Figure 5.1.1 - Layers of Skin: The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures.
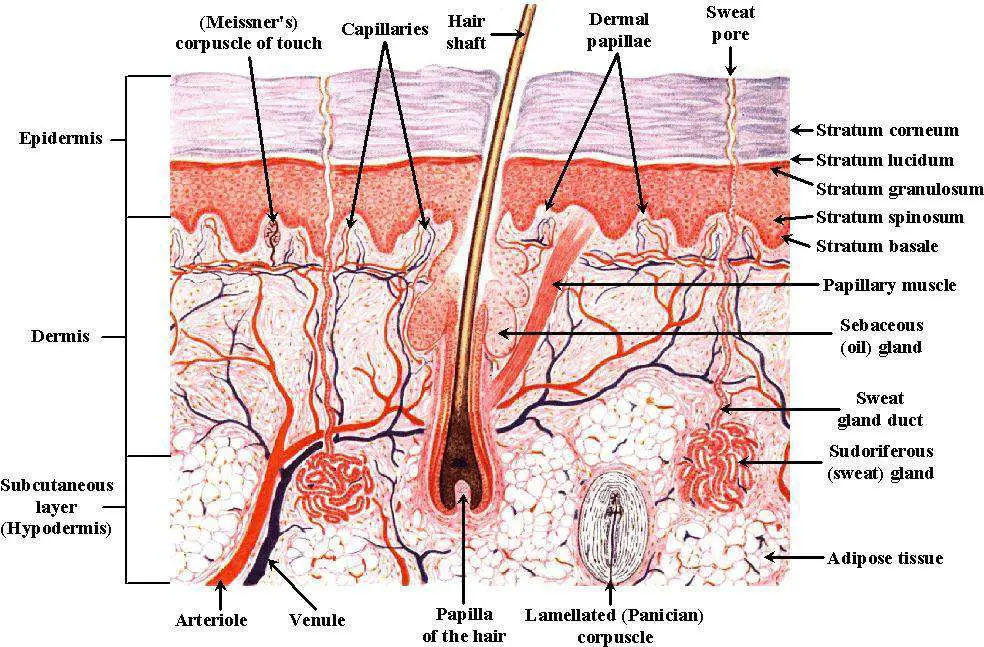
Skin diagram labeled
Anatomy of the Skin Skin Facts about the skin The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also: Regulates body temperature Stores water and fat Is a sensory organ Prevents water loss Prevents entry of bacteria

The skin Understanding cancer Macmillan Cancer Support
Figure 1. Layers of Skin. The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures.

Human Anatomy Diagrams To Label koibana.info Skin anatomy, Human anatomy, Anatomy organs
Anatomy of the Skin Click Image to Enlarge Facts about the skin The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also: Regulates body temperature Stores water and fat Is a sensory organ Prevents water loss Prevents entry of bacteria

Some curiosities about the skin Periérgeia
This article will describe the anatomy and histology of the skin. Undoubtedly, the skin is the largest organ in the human body; literally covering you from head to toe. The organ constitutes almost 8-20% of body mass and has a surface area of approximately 1.6 to 1.8 m2, in an adult. It is comprised of three major layers: epidermis, dermis and.

Structure Of Skin Skin Structure and Function LearnFatafat
The Epidermis The epidermis is composed of keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. It is made of four or five layers of epithelial cells, depending on its location in the body. It does not have any blood vessels within it (i.e., it is avascular). Skin that has four layers of cells is referred to as "thin skin."

Dermatology Diagram Show Human Skin Structure Stock Illustration Download Image Now Anatomy
The Epidermis The Dermis Hypodermis The number of skin layers that exists depends on how you count them. You have three main layers of skin—the epidermis , dermis, and hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue). Within these layers are additional layers. If you count the layers within the layers, the skin has eight or even 10 layers.